PRE-COMMERCIAL PROCUREMENT
Nowadays, the public sector has to face many societal challenges. To address these challenges, new and more sophisticated solutions, not available on a market yet, are very often required. There is a need to implement such solutions to keep or even raise the competitiveness of our market and quality of life (EC, 2013). Very important is not only to support R&D, but as said European Commissioner Viviane Reding, "Europe must create a commercial environment that encourages more rapid innovation and take up of research results." (EC, 2006)
After many dialogues and discussions, the new approach: pre-commercial procurement (henceforth: PCP) has been developed (Commission of the European Communities, 2007). This approach supports cooperation between public and private sector when creating innovative solutions with the aim to solve socio-economic problem, react to challenges or to public concern, and for which there is no solution available on a market yet that could be procured through traditional commercial procurement. In order to integrate R&D into procurement, a new phases before commercial procurement has been created (EC, 2006). For this approach especially the use in R&D field, in terms of separating primary from mass production, sharing potential risks and benefits, and finally selecting of suppliers in each phase based on competition principles are characteristic (Commission of the European Communities, 2007). This new approach can lead to stimulation of innovations, increasing the level of investment and reducing risk through co-financing, allows to stimulate the innovations, increase the level of investment and reduce risk through co-financing (Progr-EAST, 2013) where finance are used for high-risk investment projects related with difficult predictability of R&D results. PCP could be the right solution to long-term lack of cooperation between private sector in R&D field and public sector that is in position of buyer of new technologies, what confirmed also the experiences by Asian and USA. One of the best known examples of the procurement of research and development, undertaken by public bodies is the Small Business Innovation Programme (SBIR) of the United States of America which is not PCP in the sense in which it is meant though in the European Union however, but we can clearly see there efects of scuh activities. (Manchester Institute of Innovation Research, University of Manchester, 2013)
Basically, the idea of PCP is to drive technological innovation from the demand side by sharing the risks and benefits from R&D between a single purchaser and a plurality of independent providers, each awarded a separate contract for such activities as solution exploration and design, prototyping, and/or development of a limited volume of first products or services in the form of a test series. This requires a multi-stage selection described below, which is usually followed with PPI, when developed solution is commercializing. As the whole idea of innovation creation using PCP comes before first phase of PCP starts, also Phase 0 has been added.
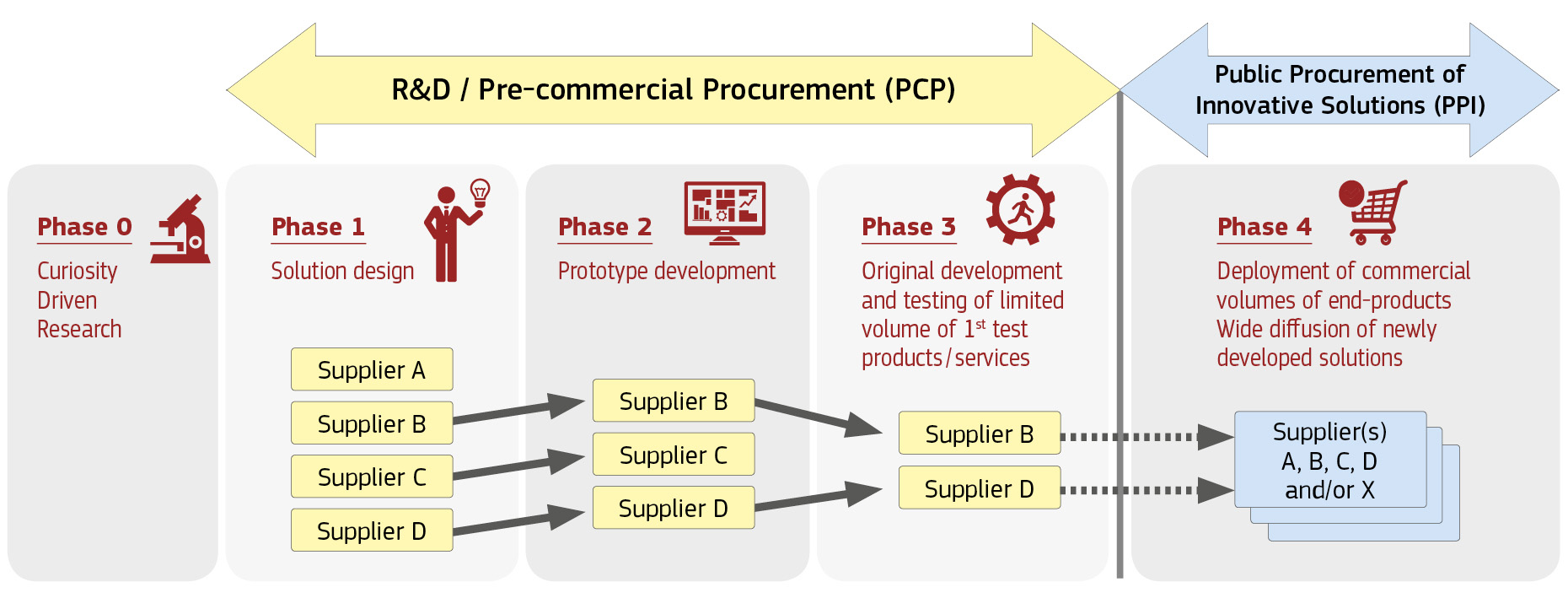
Pre-Commercial Procurement is so used when public authorities are looking for new solutions to actual problems, which is clearly defined, but pros and cons of potential solutions are not known yet. In such a situation public sector can buy R&D from several suppliers in parallel (comparing alternative solution approaches), in form of competition evaluating progress after critical milestones (design, prototyping, test phase), risks & benefits of R&D (e.g. IPRs) shared with suppliers to maximise incentives for wide commercialisation. As next possible step, after final phases of innovation development, there can come Public Procurement of Innovative Solutions (PPI). PPI is specifically focused on popularization of new inventions, from process of PCP, as they could be deployed on the market in a large volume.


